Data Mining
Summary of lectures
Lecture 1 - 18/09/2018
- Data Mining:
- Data processing using sophisticated data search capabilities and statistical algorithms to discover patterns and correlations in large preexisting databases; a way to discover new meaning in data.
- The process of extracting patterns from data. It is commonly used in a wide range of profiling practices, such as marketing, surveillance, fraud detection and scientific discovery.
- A technique for searching large-scale databases for patterns.
- The process of identifying and extracting patterns from data, particularly from very large and/or complex sets of data.
- A method of comparing large amounts of data to find patters. Normally this is used for models and forecasting.
- Datamining (or data acquisition) is the process of autonomously retrieving useful information or knowledge (“actionable assets”) from large data stores or sets.
- The extraction of patterns and other useful information from a corpus of data.
- The process of analysing data in order to determine patterns and their relationships.
- Using computers to analyze masses of information to discover trends and patterns.
- Is the exploration and analysis of data in order to discover patterns, correlations and other regularities.
- Data Mining (Methods + Applications)
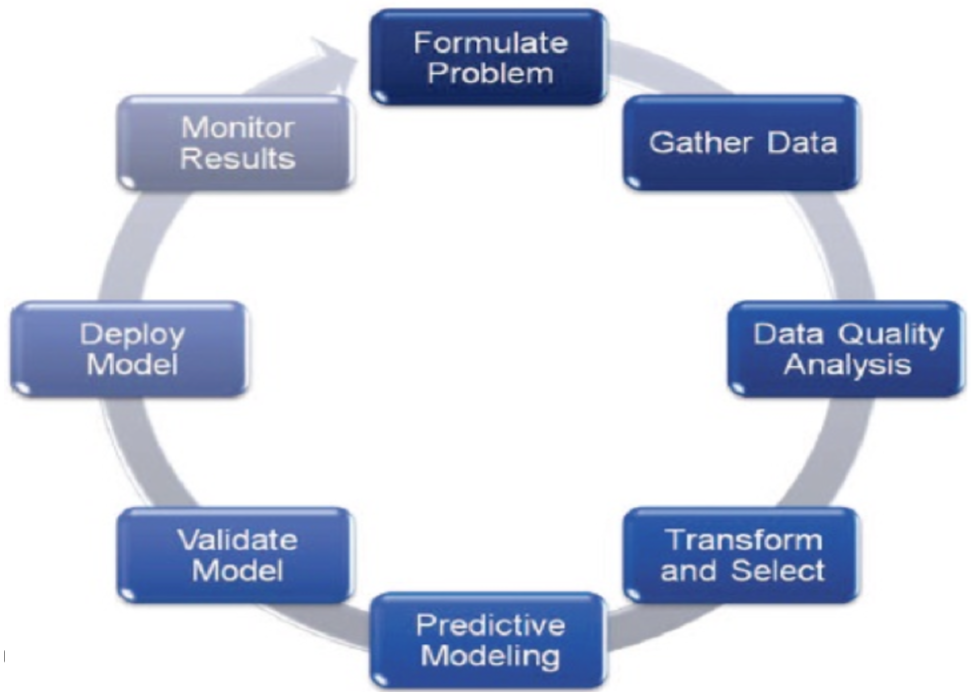
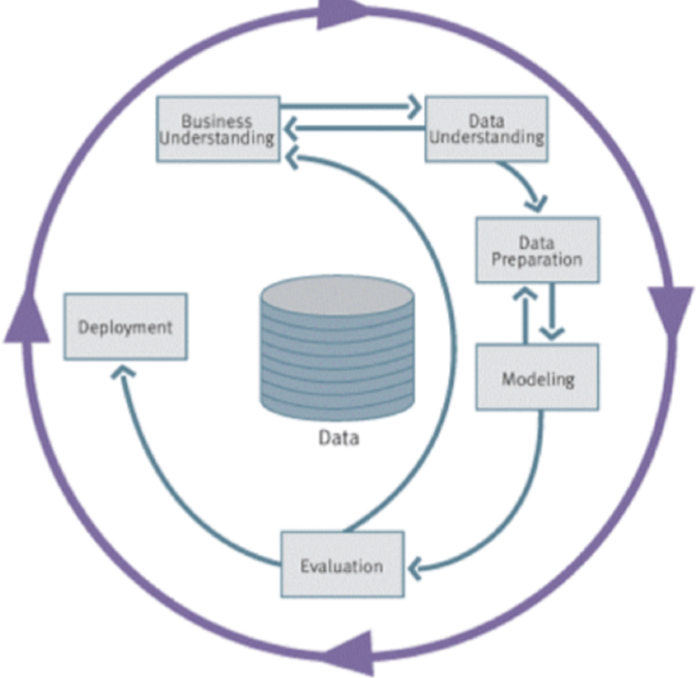
- Looks at defining the business question being investigated, what data is related to that question, understanding that data, identifying appropriate techniques to use (eg. ML), analysing the results generated to apply domain knowledge, being able to related this back to the business, understanding how the results/models etc can be incorporated into the business processes, and monitor & updating the processes based on their performance on live data.
- Looking to solve business problems
- Combining many different technologies
- Requires the human brain
- Business understanding
- How findings relate to business
- Looks at defining the business question being investigated, what data is related to that question, understanding that data, identifying appropriate techniques to use (eg. ML), analysing the results generated to apply domain knowledge, being able to related this back to the business, understanding how the results/models etc can be incorporated into the business processes, and monitor & updating the processes based on their performance on live data.
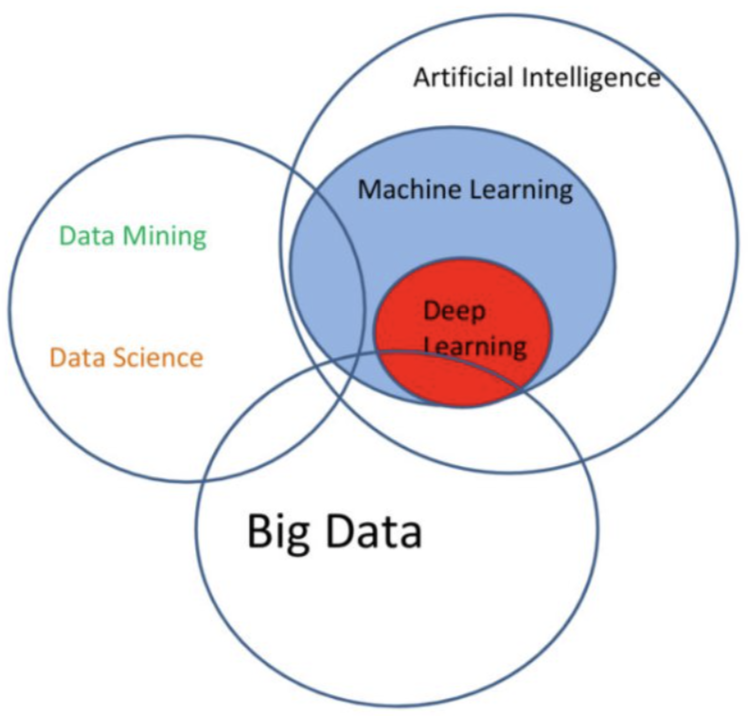
- Machine Learning (Theory + Methods)
- Focuses on the algorithms, how these work, how they can be customised, how they can be tuned, finding or discovering how they can be used in new situations.
- Machine Learning is only one component(*) of Data Mining. (And only one of the tools you can use for the Modeling / Predictive Analytics phase)
- Coding of algorithms
- Designing of algorithms
- Finding applications areas
Lecture 4 - 09/10/2018
Text Mining – Part 2. Opinion Mining / Sentiment Analysis. Combining Text procession with Machine Learning.
- Sentiment analysis or opinion mining.
- Computationalstudyofopinions, sentiments, evaluations, attitudes, appraisal, affects, views, emotions, subjectivity, etc., expressed in text.
- Reviews, blogs, discussions, news, comments, feedback,oranyother documents.
- Terminology:
- Sentiment analysis is more widely used in industry.
- Opinion mining.
- But they can be used interchangeably.
- Natural language processing (NLP).
- It deals with the actual text element. It transforms it into a format that the machine can use.
- Artificial intelligence.
- It uses the information given by the NLP and uses a lot of maths to determine whether something is negative or positive.
- Tokenization
- is the process of breaking a stream of text up into words, phrases, symbols, or other meaningful elements called tokens.
- stop words
- are words which are filtered out prior to, or after, processing of natural language data (text).